Linux System Monitoring Commands like " top, free, watch, df, du, vmstat, ps and renice "
In Linux there are some common commands we use for System Monitoring, Let us see one-by-one ...
That's it for now ... I'll update this post if i'll find any thing else interesting.
_Enjoy :)
To check:
Process listing
Free/available memory
Disk utilization
- #top : Shows combination of ps, uptime, free and updates regulary, Press "Q" to come out of it.
- #free -m : Shows RAM, SWAP memory utilization in human readable formate i.e. in MB
- #df -h : Shows disk partitions, mount points in human readable formate i.e. in MB
- #du -h : Shows size of every child file & folder of a parant folder
- #vmstat : shows info about processes, memory, paging, block I/O, traps, CPU consumption
- #gnome-system-monitor : Shows GUI System Monitoring Tool
- #runlevel : Shows Previous & current runlevel
- #ps -ef : This will display process status and listing with process ID.
- #kill -9 <PID> : Used to kill any unwanted process.
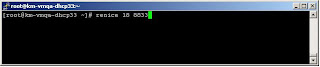
- #renice <Priority No.> <PID> : Used to change priority of any process. Priority number can be between 1-19, Higher the value lower the priority.
- #watch <Command> : Execute that command in every 2sec. defualtly, Press Ctrl+c to exit e.g.
#watch df -h
Note :
- Keep monitoring /tmp folder space, if it gets full then might encounter some performance issue.
- Keep monitoring total swap space.
- Keep monitoring /root partition space.
- You can check CPU & Memory related info from
#cat /proc/cpuinfo
#cat /proc/meminfo - Always use ext3 file system for better disk performance. Also called as Journaling File System.
- Remove unwanted services for better system performance. You can do this by using "chkconfig" command,
#service <Service Name> <stop>
#chkconfig <Service Name> <off>
To Start any service permanently,
#service <Service Name> <start>
#chkconfig <Service Name> <on>
That's it for now ... I'll update this post if i'll find any thing else interesting.
_Enjoy :)










Comments
Post a Comment