Recovering or restoring grub in CentOS or RHEL 7
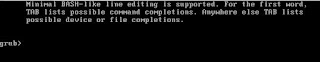
What if GRUB is corrupted on your RHEL or CentOS 7 ? GRUB corruption is a common problem in RHEL or CentOS, which could occur due these reasons: If any file is missing or deleted from "/boot/grub2/" folder e.g. "grub.cfg" Mistakenly ran "dd" utility to clear boot sector Due to bad sector or corrupted disk Bad or incompatible firmware/driver installation e.t.c. In case GRUB is corrupted, usually after powering on your server you see below kind of shell, also known as GRUB shell: Once you get to this prompt there is a way to restore or recover GRUB so that your system can boot up properly. To recover GRUB we need to have RHEL or CentOS 7 ISO image, which we usually use for OS installation. Make sure you mount same OS version iso image which is already installed on system. Below procedure will work only on BIOS based X86 servers and virtual machines. Follow these steps to recover GRUB: Step 1 : Mount RHEL or CentOS 7 ISO image ...
